Activated Sludge Process: The Engine of Wastewater Treatment
Jan 14, 2026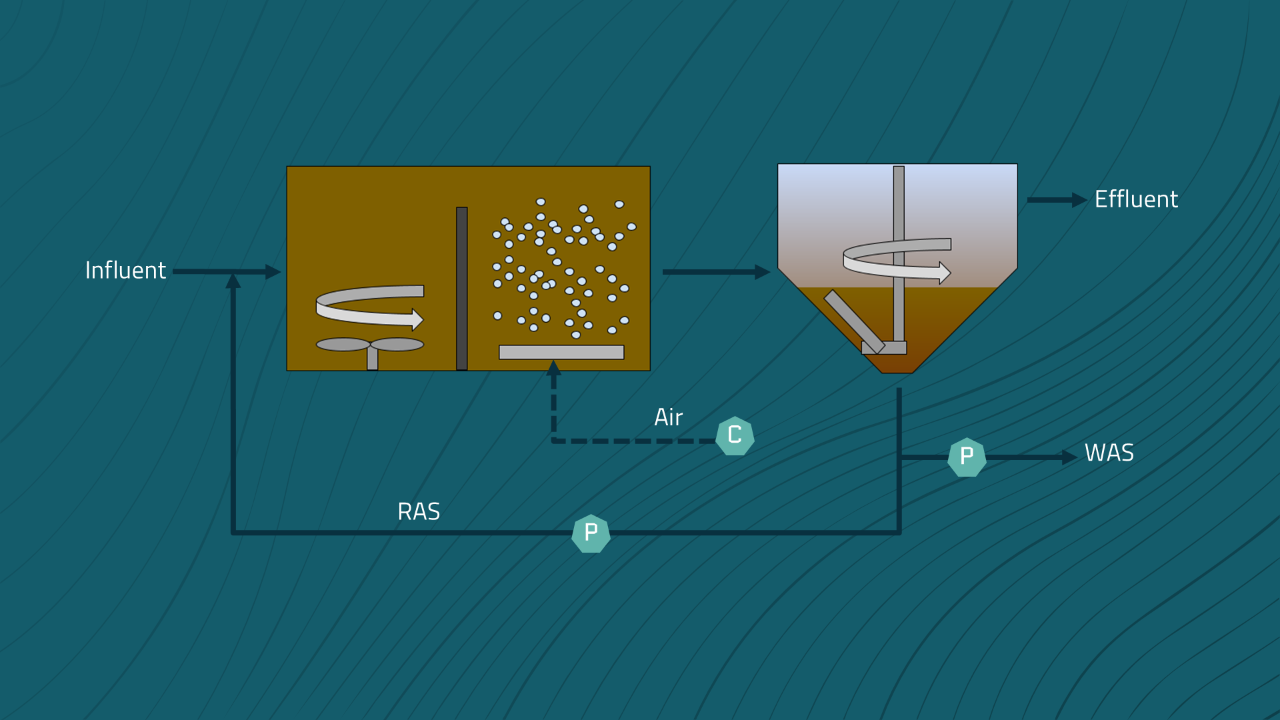
Understanding the major components in the activated sludge process is essential for sustainable team/facility management and individual professional growth. Ultimately, for a facility this knowledge translates into permit compliance, cost efficiency, and proper emergency response. The activated sludge process includes five basic components which are illustrated in the figure above and summarized as follows:
The Activated Sludge Process includes five main components:
- Provides the physical space for the biological reactions to occur. The contents of the reactor are called Mixed Liquor or Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids (MLSS). The reactor is typically made of concrete or steel.
- Aeration System. Produces and delivers the air (oxygen) to the microbes in the Reactor. The system is made up of blowers/compressors, piping, and diffusers.
- Separates the biological solids (MLSS) from the treated water. The system is made up of a concrete or steel tank and internal mechanisms to promote settling.
- RAS System. The Return Activated Sludge (RAS) system collects and returns the biological solids from the clarifier back to the Reactor. The system is made up of pumps and pipes.
- WAS System. The Waste Activated Sludge (WAS) system removes (or “wastes”) a portion of the biological solids from the system. This is done to maintain the health and performance of the activated sludge process. The system is made up of pumps and pipes
A solid understanding of treatment Basics like this keeps operations teams grounded. For those new to the industry, this information is the foundation of future knowledge and skills in a very rewarding career. For more senior professionals, it can be a welcomed refresher in an industry that is constantly changing/ evolving. I have numerous courses that cover the basics of wastewater treatment, and am pleased to offer 20% off for a limited time. Download it here.
