The Blog
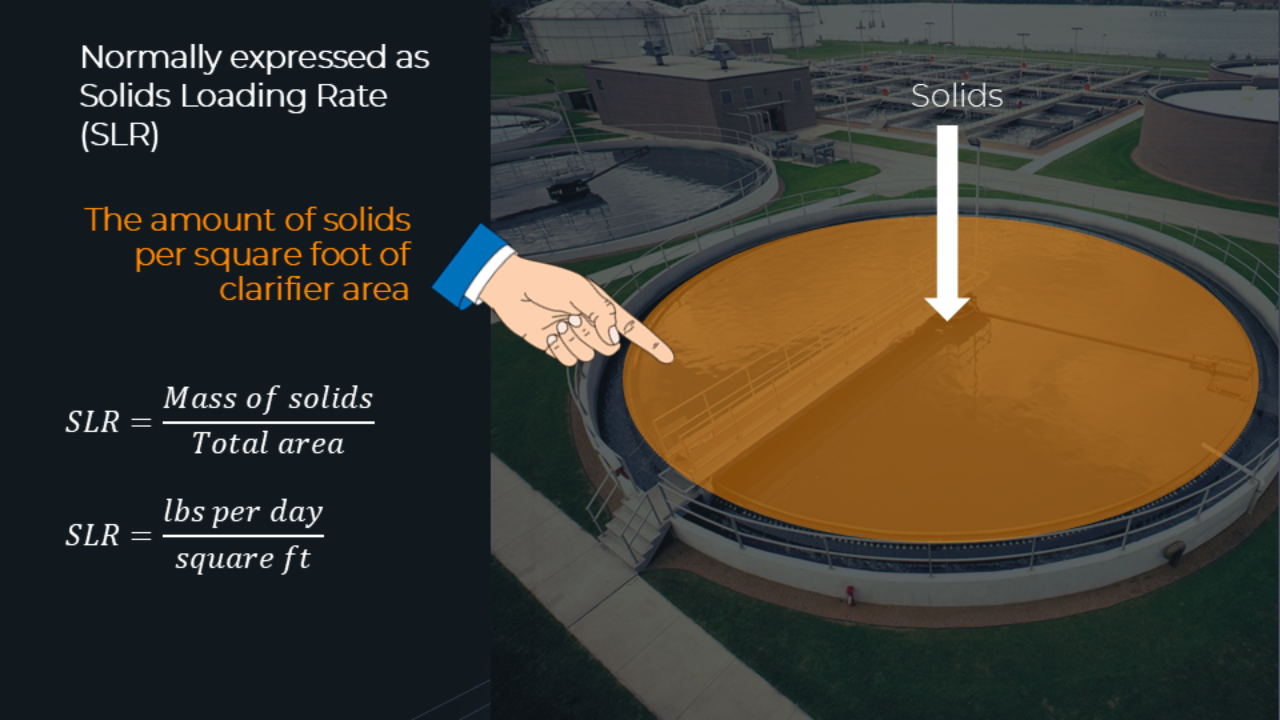
Solids Loading Rate (SLR) is how we measure the solids loading to a clarifier. It’s calculated by dividing mass of solids (TSS) sent to the clarifier by the clarifier surface area. Typical values are ...
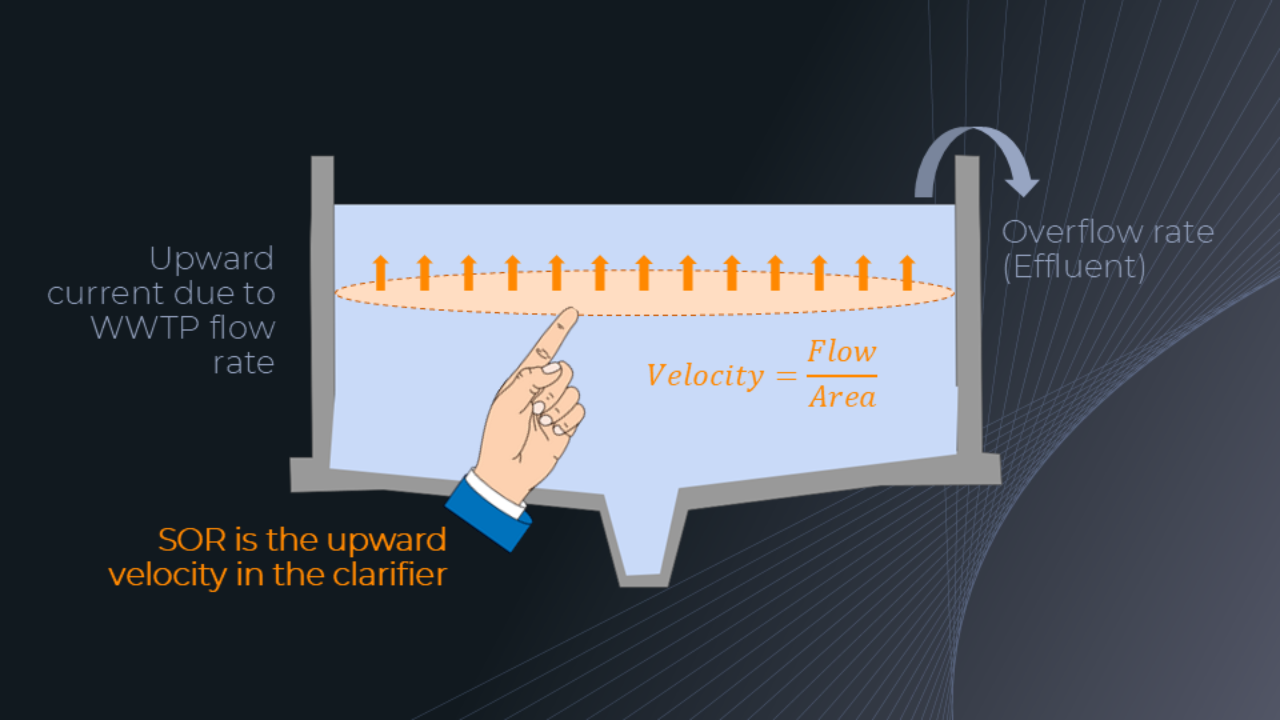
Surface Overflow Rate (SOR) is how we measure the hydraulic loading for a clarifier. It’s calculated by dividing effluent flow of a clarifier by the clarifier surface area. Typical values are 800 ga...
Hydraulic Retention time (HRT) is the theoretical time a drop of water remains in a clarifier. It’s calculated as clarifier volume divided by effluent flow rate. Clarifier HRT is typically 3 to 6 hou...
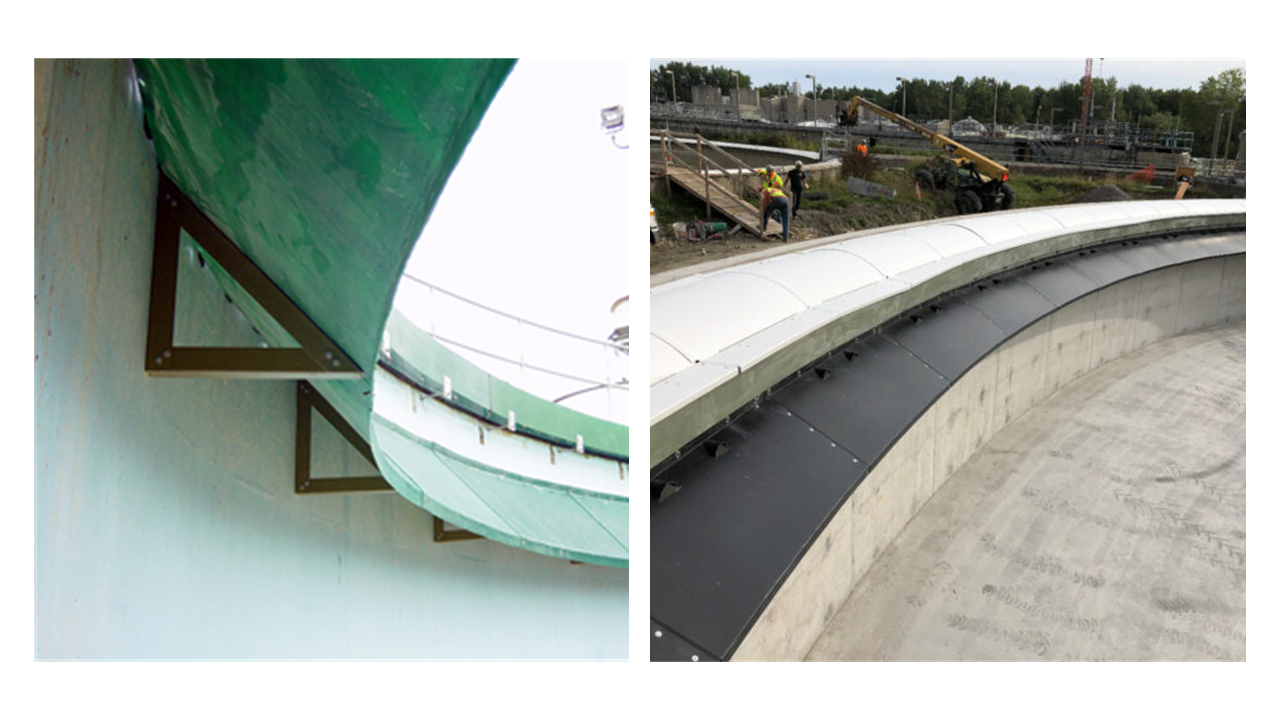
Baffles are structures within clarifiers that disrupt short-circuiting and slow currents to improve settling performance. In circular clarifiers, mid-tank baffles (Crosby cylindrical) and angled baffl...
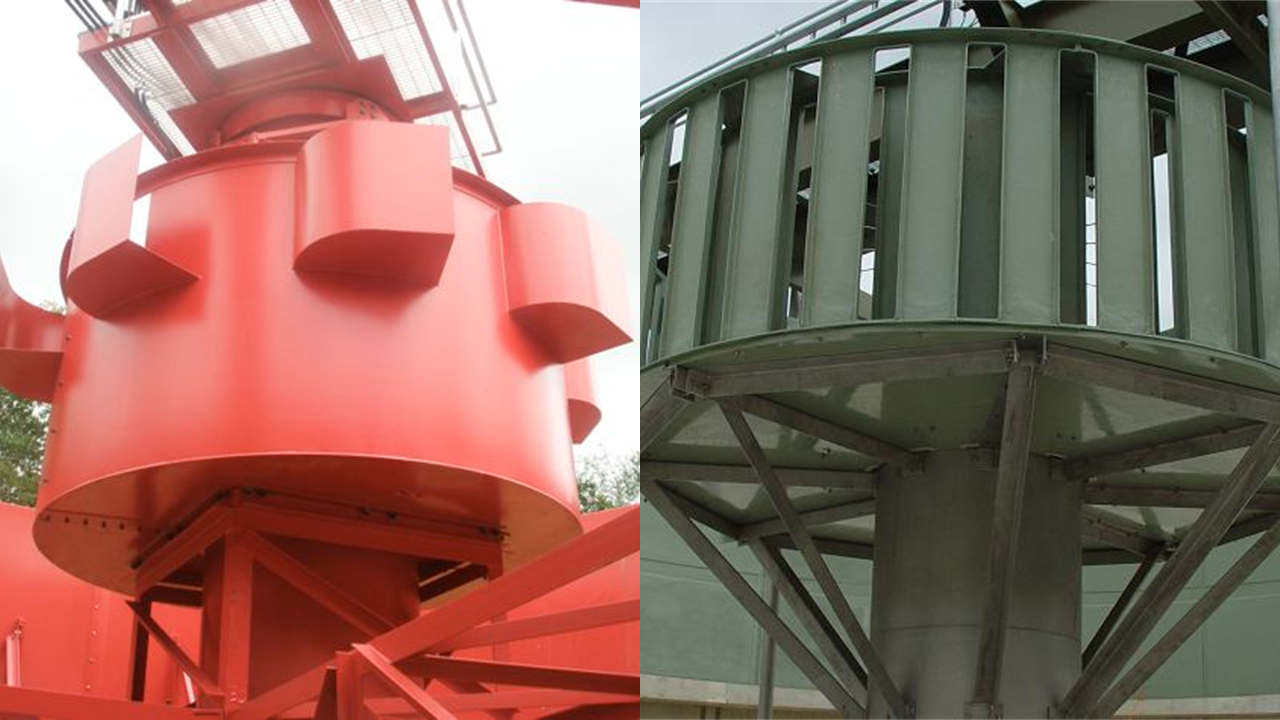
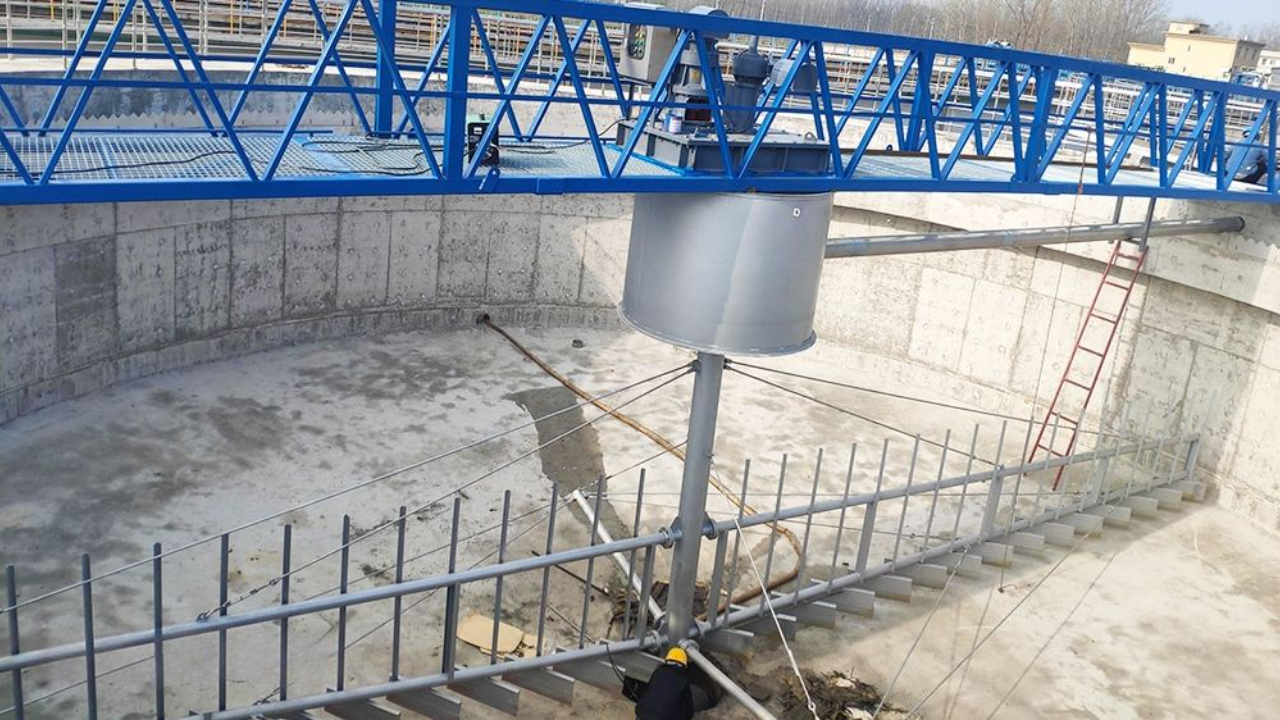
An Energy-dissipating inlet (EDI) is a device placed inside the feedwell. It helps dissipate the energy (velocity) of incoming influent to promote flocculation. EDIs eliminate flow currents from occu...
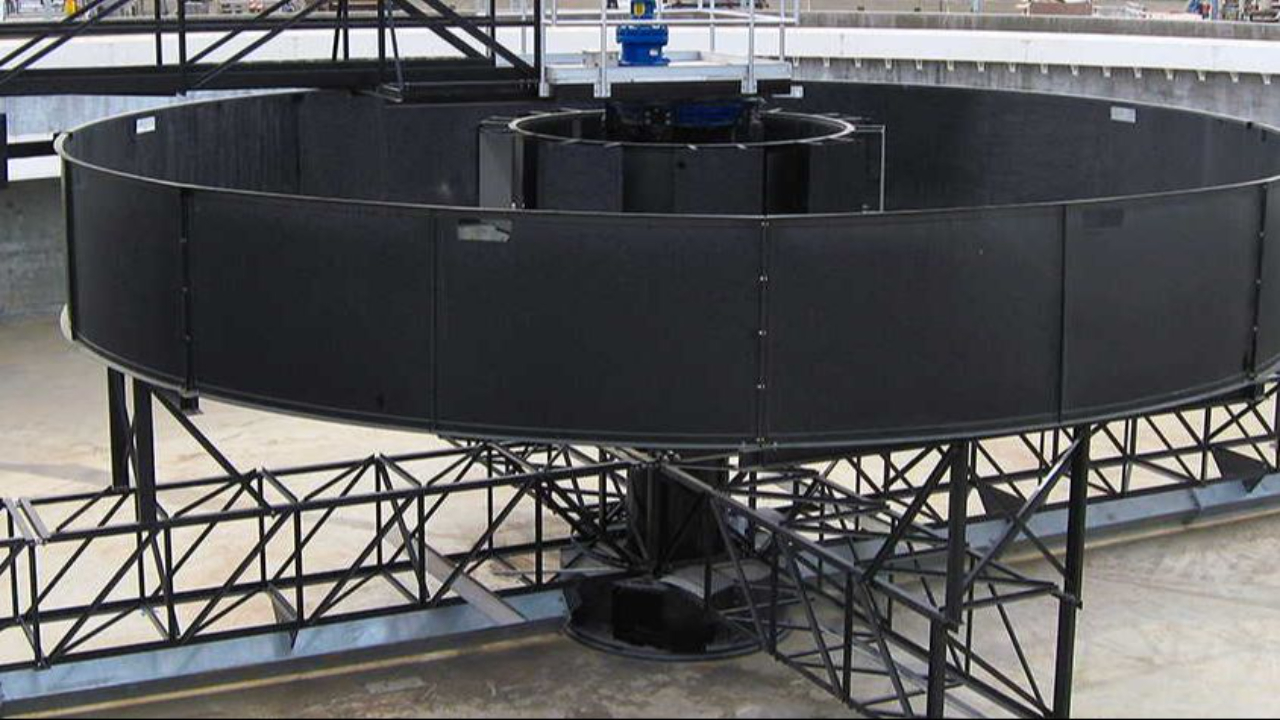
The feedwell in circular clarifiers is a cylindrical structure around the center feed column that aids in flocculation and flow distribution. It should be large enough to prevent concentrated downward...
Scum-collection systems in clarifiers remove floating material from the surface and typically include a scum baffle, skimmer arm, and scum trough. Circular clarifiers use skimmer-arm squeegees and dee...
Solids collectors collect and help remove settled biomass from the bottom of clarifiers. Circular clarifiers use devices like scrapers, suction headers, and withdrawal tubes, while rectangular ones ty...
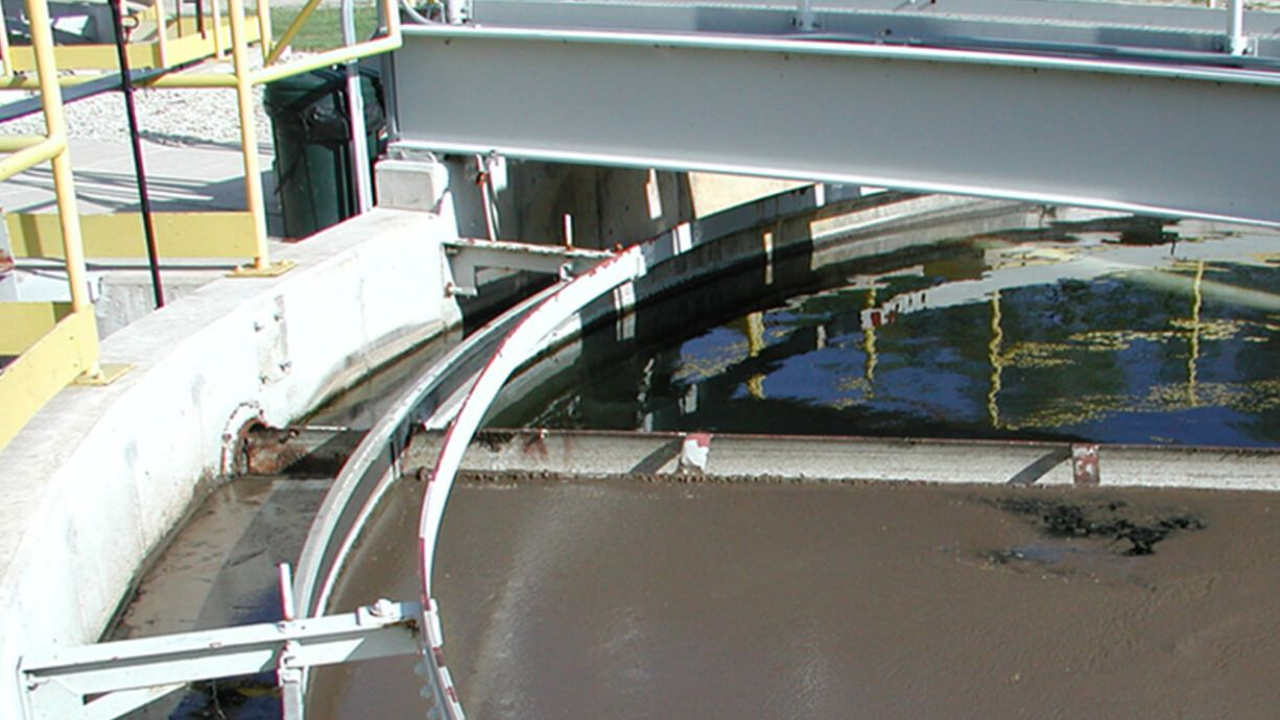
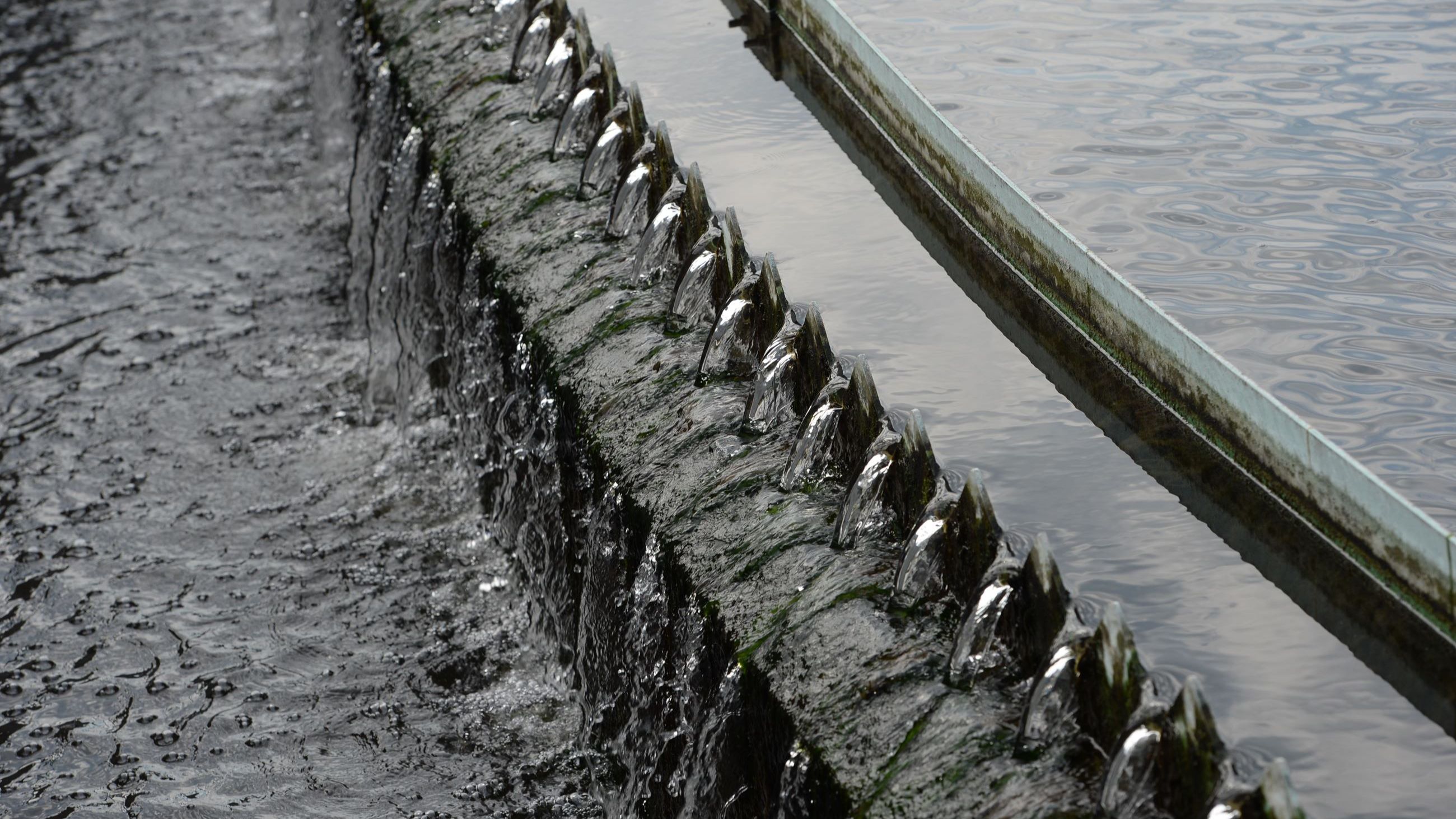
A weir is a plate used to control flow from a clarifier. Specifically, it makes sure the flow is evenly applied across the whole tank. Clarifier weirs often have v-shape notches. Proper leveling and...
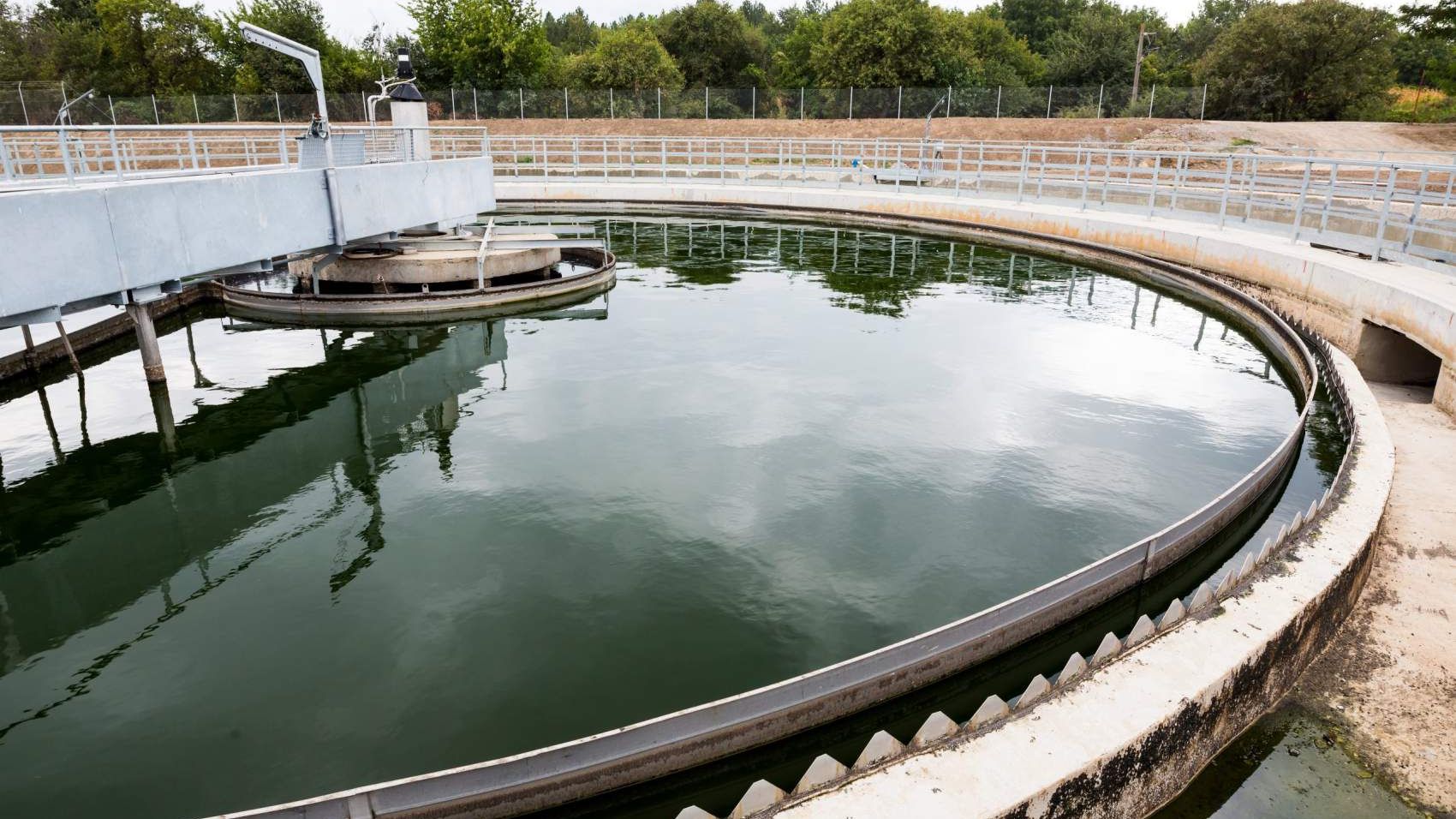
Secondary clarification is essential in biological wastewater treatment, especially in suspended growth systems. Its main purpose is to separate the biological floc (biomass) from the treated liquid. ...
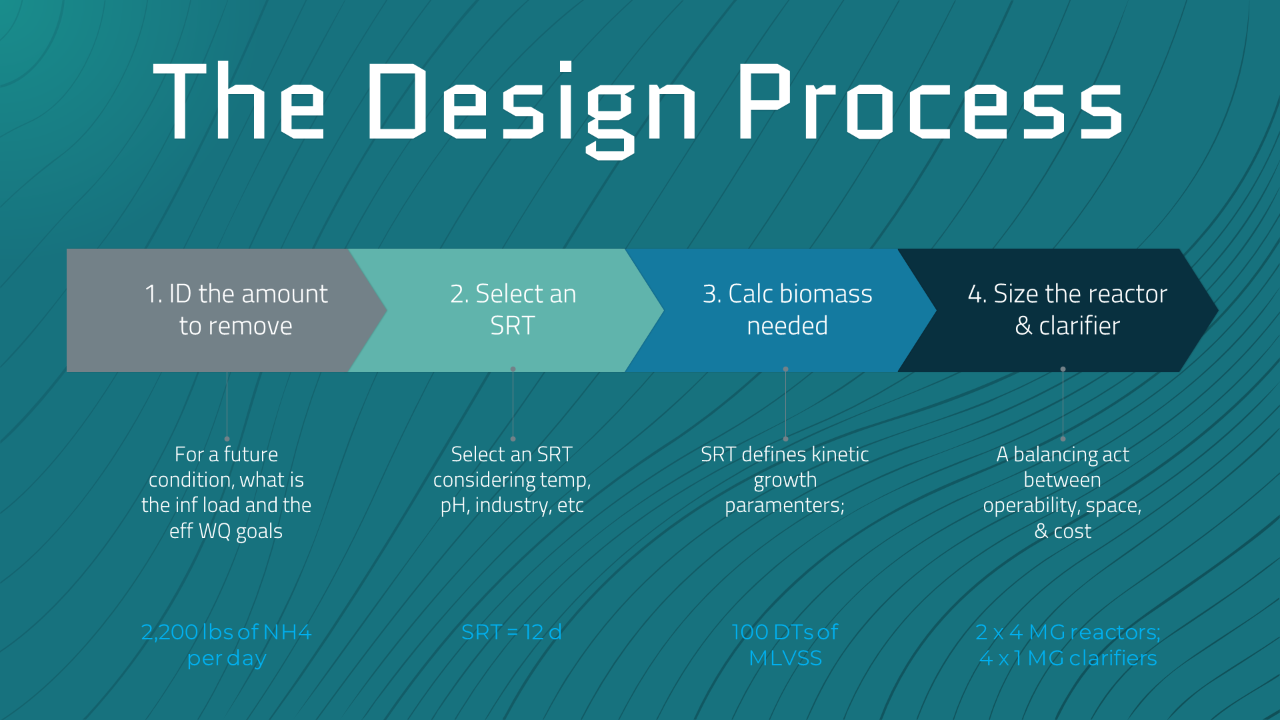
The O&M manual and/or design drawings for a wastewater treatment facility should include a basis of design documenting the design SRT, MLSS concentration, and F:M ratio, along with Raw influent flows ...
There are three key biological design variables for the activated sludge process: Solids Retention Time (SRT), mixed Liquor Suspended Solids (MLSS) concentration, Food to Mass Ratio (F:M). Either can ...