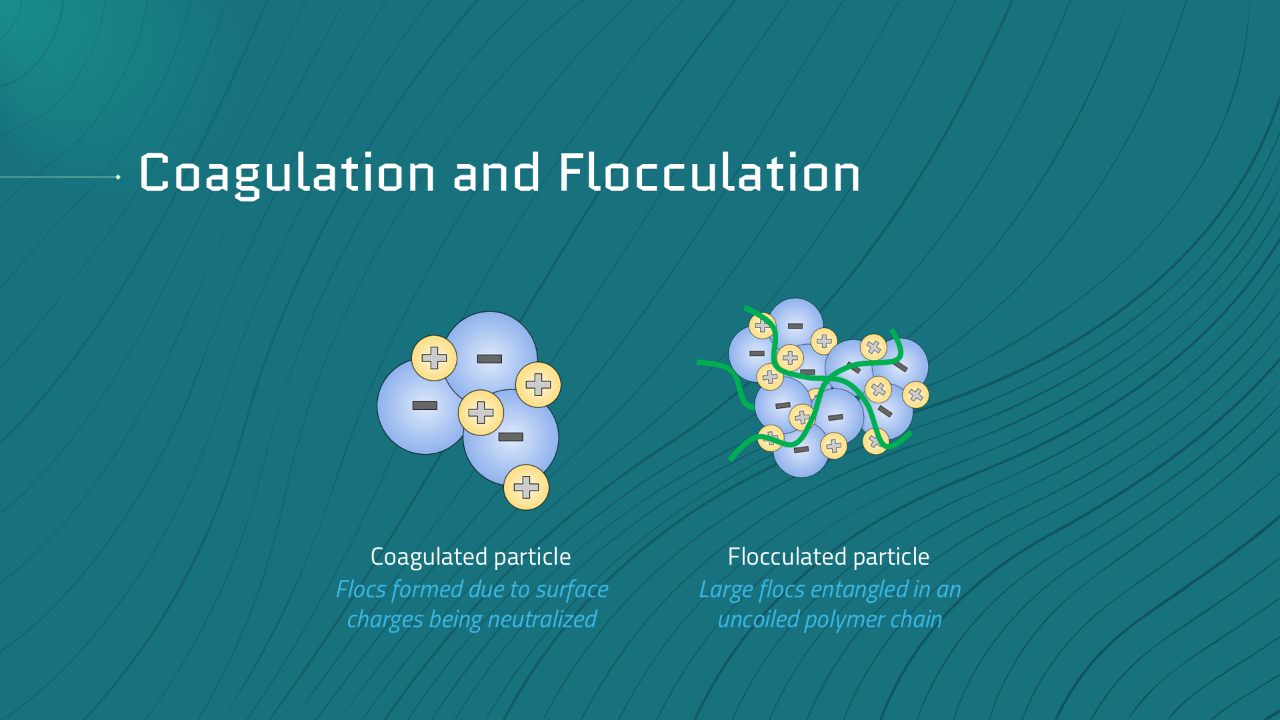
The Blog
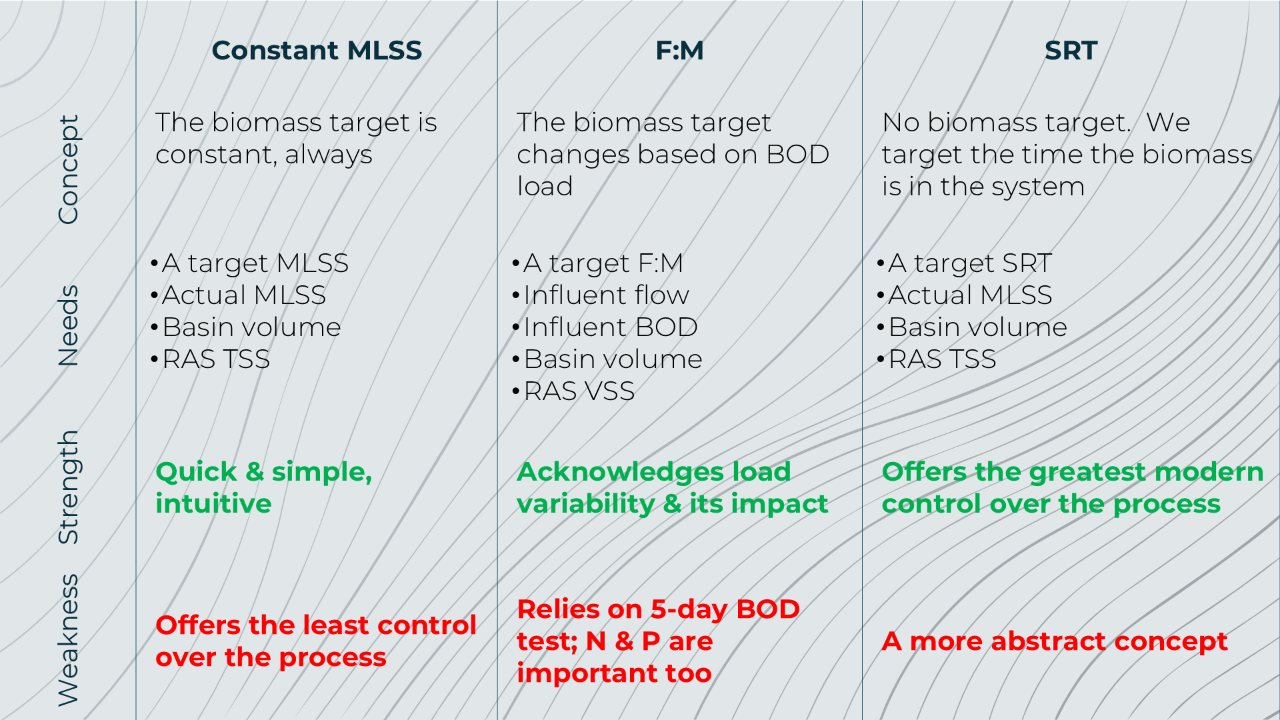
Understanding different wasting control strategies helps operators respond effectively to changing conditions, maintain effluent quality, and manage costs. A deeper knowledge turns the routine task of...
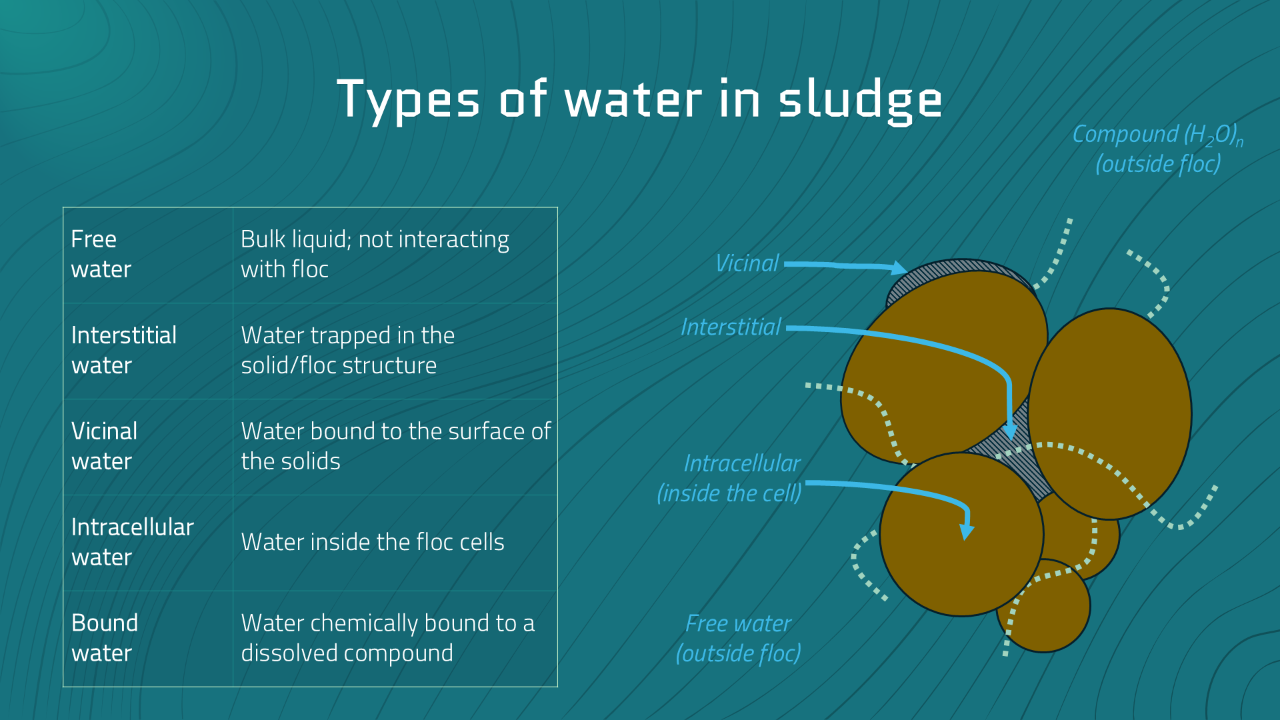
Thickening and dewatering are bookends of your residuals handling process. Your operational knowledge/skill here has direct, whole-plant impacts including treatment performance, permit compliance, an...
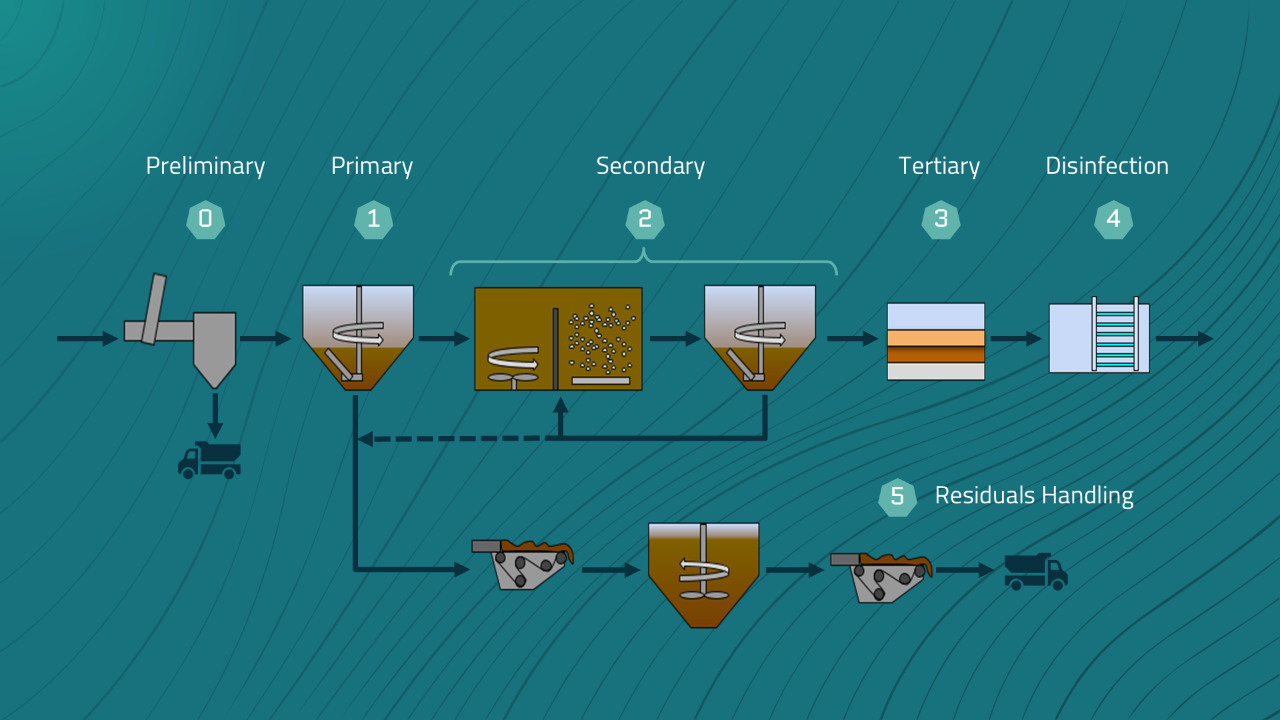
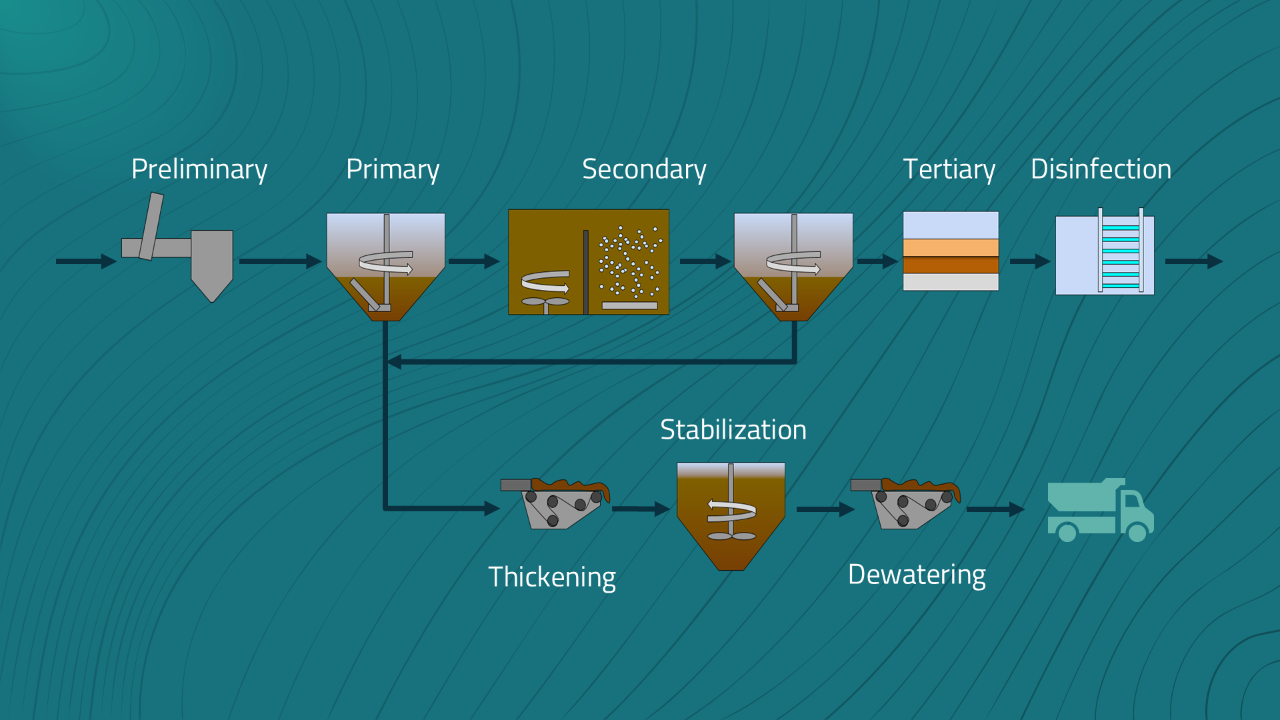
Understanding the major steps in wastewater treatment is essential for sustainable team/facility management and individual professional growth. Ultimately, for a facility this knowledge translates in...
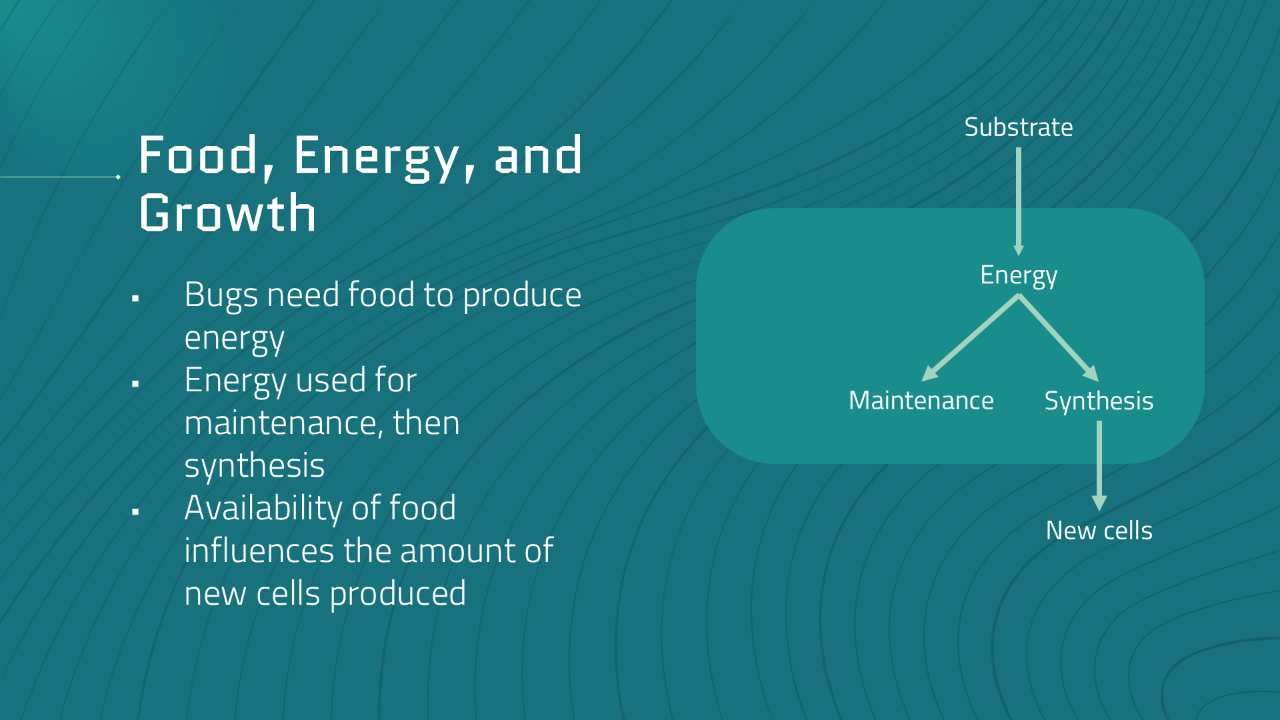
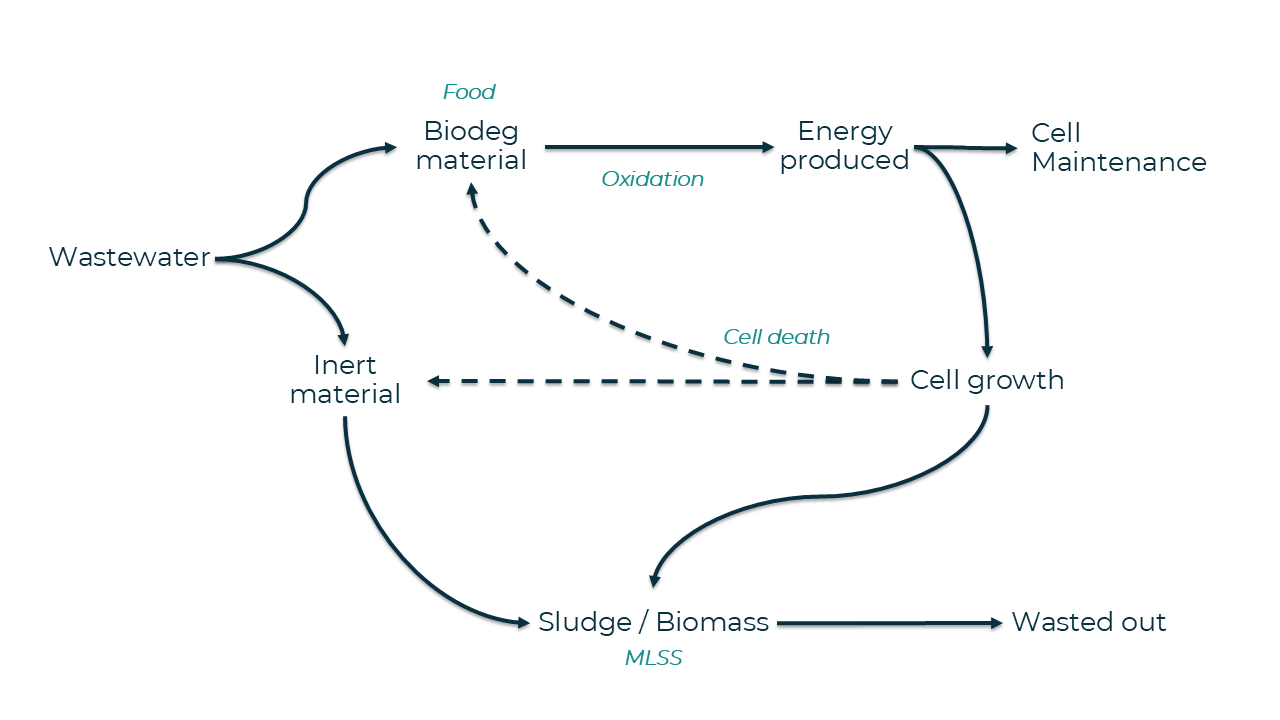
Understanding how microbes use energy fosters a deeper understanding of microbial behavior and empowers operators to make smarter, more strategic decisions that optimize plant performance. In the acti...
Thickening and dewatering are bookends of your residuals handling process. Your operational knowledge/skill here has direct, whole-plant impacts including treatment performance, permit compliance, an...
Thickening and dewatering are bookends of your residuals handling process. Your operational knowledge/skill here has direct, whole-plant impacts including treatment performance, permit compliance, an...
Secondary clarifier capacity changes in step with how well the mixed liquor settles. So, having insight into that settleability helps us understand how much flow the clarifiers can handle before bad ...
Understanding the factors that affect sludge production fosters a deeper understanding and equips operators to respond proactively to daily system changes which ultimately translates to consistent reg...
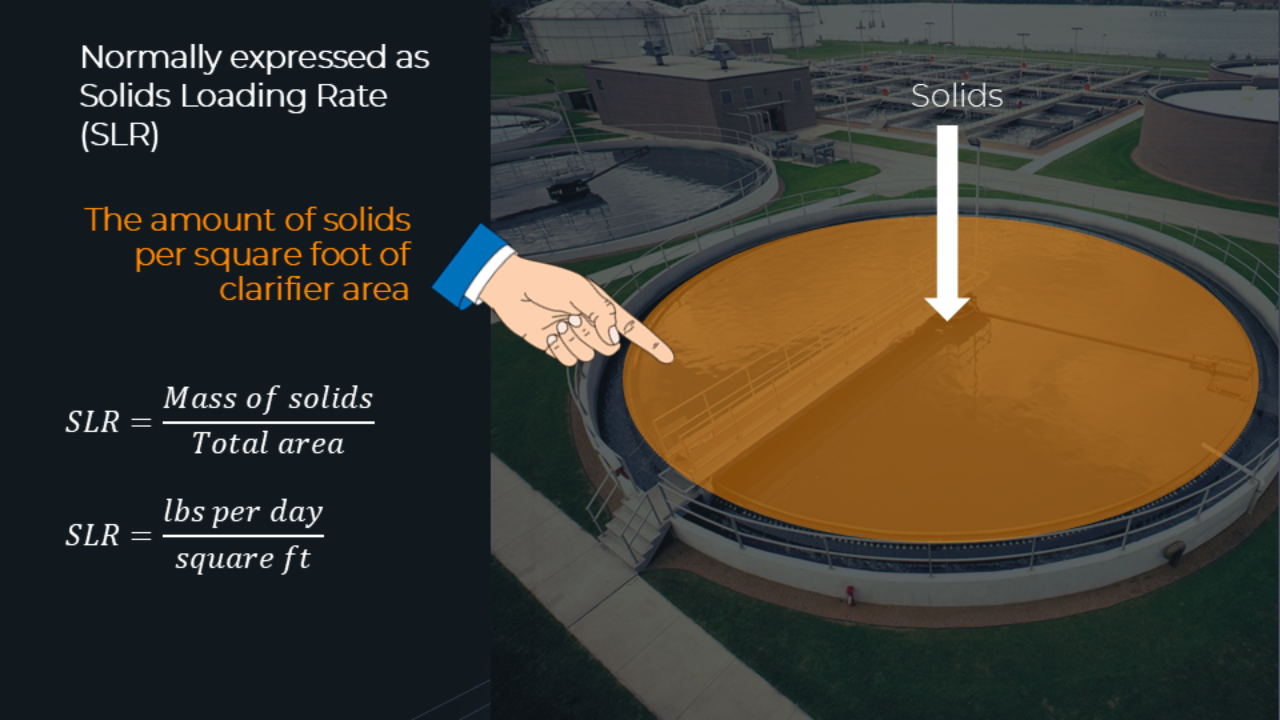
Solids Loading Rate (SLR) is how we measure the solids loading to a clarifier. It’s calculated by dividing mass of solids (TSS) sent to the clarifier by the clarifier surface area. Typical values are ...
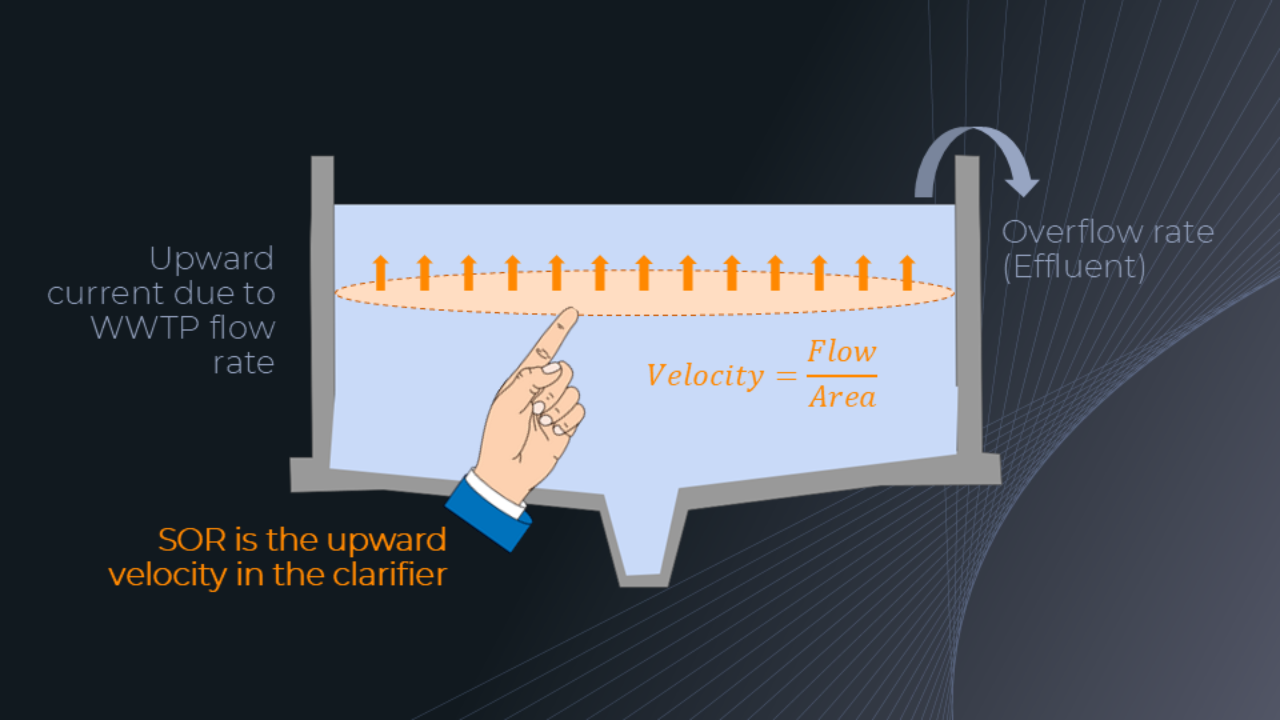
Surface Overflow Rate (SOR) is how we measure the hydraulic loading for a clarifier. It’s calculated by dividing effluent flow of a clarifier by the clarifier surface area. Typical values are 800 ga...
Hydraulic Retention time (HRT) is the theoretical time a drop of water remains in a clarifier. It’s calculated as clarifier volume divided by effluent flow rate. Clarifier HRT is typically 3 to 6 hou...
Baffles are structures within clarifiers that disrupt short-circuiting and slow currents to improve settling performance. In circular clarifiers, mid-tank baffles (Crosby cylindrical) and angled baffl...